First off, I am no expert in Natron Digital Compositor. However, I have created some basic compositing using it and found it fairly intuitive.
Hence, I am creating a very basic introduction to this free, open source 2D Digital Compositor.
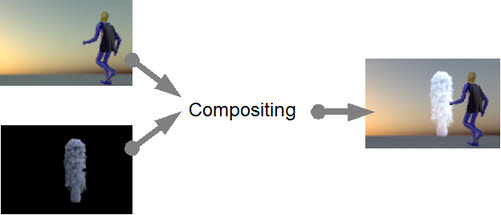
Natron is a node-base digital compositor. Composite Nodes are individual blocks that perform a certain operation. Compositing Nodes allow you to take multiple renders, videos, images and other sources as inputs, and process a variety of operations on them to combine them in different ways.This process is not unlike what an Image Editor (such as GIMP or Photoshop) does. However, unlike generic 2D image editing, Node Compositing allows the ‘batch’ compositing of all frames within an animation.
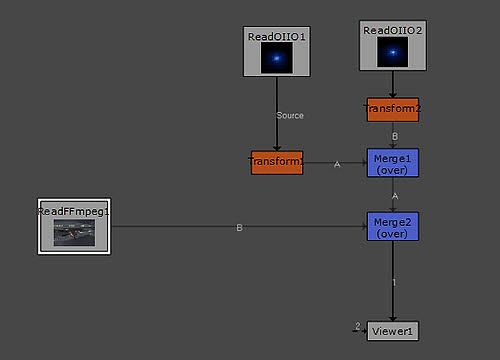
Node setups will look like blocks connected by lines (arrows). Below shows an example of a Node configuration.
Accessing Compositing Nodes
All node types are accessed via the Main Icons on the left side of the Natron GUI. To add a Node onto the Node Graph Window, simply navigate the cursor to intended icon/label.

Each Node consists of a corresponding Properties Panel which is usually situated on the right side of the GUI. Below shows a Read Node and its corresponding Properties Panel.
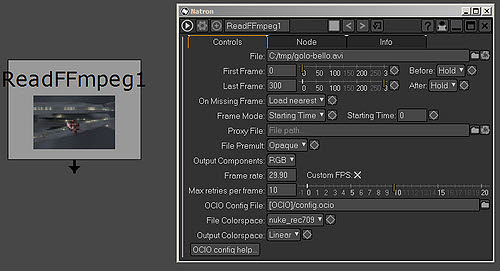
These properties panels are used to control parameter or even add keyframes for animations.
To find the Properties Panel of a node, double-click that Node in the Node Graph Window.
>>> Click here to go to Part 2 – Basic Introduction to Natron for Digital Compositing
